Introducción
El rand sudafricano ocupa una posición privilegiada en el trading de divisas, ya que es un indicador vital de las tendencias económicas de los mercados emergentes. Este artículo se sumerge en la rica historia y las implicaciones económicas del rand sudafricano, destacando su papel en las finanzas mundiales y en los entornos de trading. Al comprender la evolución de esta divisa, los traders pueden navegar mejor las complejidades del mercado de divisas, utilizando la información sobre el rendimiento del rand para tomar decisiones informadas a la hora de operar.
¿Qué es el rand sudafricano (ZAR)?
El rand sudafricano (ZAR), denotado por el símbolo 'R' y subdividido en 100 céntimos, es la moneda oficial de Sudáfrica y también se utiliza en el Área Monetaria Común, que incluye a Namibia, Lesoto y Eswatini. Introducido el 14 de febrero de 1961, el rand sustituyó a la libra sudafricana como moneda de curso legal. El nombre 'Rand' deriva del Witwatersrand. En esta cresta se alza Johannesburgo, donde se encontraron los principales yacimientos de oro de Sudáfrica, lo que subraya la conexión histórica entre la riqueza del país y su moneda.
El Banco de la Reserva de Sudáfrica gestiona la emisión y regulación del rand. A lo largo de los años, la moneda ha pasado por varias fases de depreciación y apreciación, influida por las políticas económicas nacionales y los acontecimientos políticos internacionales. Desde su creación, el rand ha reflejado la resistencia y los retos económicos de Sudáfrica, reaccionando a menudo de forma brusca ante los cambios mundiales y locales.
Conoce el rand sudafricano (ZAR)
El fin del apartheid
El desmantelamiento del apartheid en Sudáfrica tuvo profundas repercusiones en la economía del país y, por extensión, en el valor de su moneda. El apartheid, el sistema de segregación y discriminación racial institucionalizado, llegó a su fin a principios de la década de 1990, sentando las bases para importantes cambios políticos y económicos. La transición a un gobierno mayoritario en 1994 marcó un punto de inflexión crítico para el rand sudafricano, ya que los inversores reaccionaron con optimismo a los cambios. Las elecciones generales de 1994, que llevaron al poder a Nelson Mandela, provocaron, en un inicio, una volatilidad en el valor del rand, ya que el mercado calibraba las políticas económicas del nuevo gobierno.
El Krugerrand
Introducido en 1967, el Krugerrand es una moneda de oro sudafricana acuñada por la Casa de la Moneda de Sudáfrica para ayudar a comercializar el oro sudafricano. Debe su nombre a Paul Kruger, figura prominente de la historia de Sudáfrica y rostro de la moneda, y al rand, la divisa sudafricana. El Krugerrand fue la primera moneda de oro que contenía exactamente una onza de oro fino, y su objetivo era proporcionar un vehículo para la propiedad privada del oro. A pesar de las sanciones económicas impuestas a Sudáfrica durante los años del apartheid, el Krugerrand se distribuyó por todo el mundo y se convirtió en un medio popular para que las personas tuvieran oro. Incluso hoy en día, sigue siendo uno de los favoritos entre los inversores y coleccionistas de oro de todo el mundo.
El Banco de la Reserva de Sudáfrica
Creado en 1921, el Banco de la Reserva de Sudáfrica (SARB) es el banco central del país. Es el principal responsable de alcanzar y mantener la estabilidad de precios en beneficio de un crecimiento económico equilibrado y sostenible en el país. Como emisor del rand sudafricano, el SARB desempeña un papel crucial en la estabilidad financiera y la política económica del país.
Las funciones del banco central han evolucionado, sobre todo tras la transición de Sudáfrica del apartheid a un gobierno democrático. Una de sus funciones clave es la gestión de la moneda del país, el rand, a través de la política monetaria, que incluye la fijación de las tasas de interés y el control de la oferta monetaria. El SARB también supervisa el sector bancario, velando por su estabilidad y correcta regulción. Esta supervisión se extiende al mantenimiento de sistemas de pago eficaces y a la gestión de las reservas de oro y divisas del país.
El área monetaria del rand
El Área Monetaria Común (CMA) ilustra una importante cooperación regional en materia de gestión monetaria en la que participan Sudáfrica, Namibia, Lesoto y Eswatini. Establecida para facilitar la integración económica y el beneficio mutuo entre los países miembros, el CMA permite utilizar el rand sudafricano como moneda común. Sin embargo, cada uno mantiene también su propia moneda.
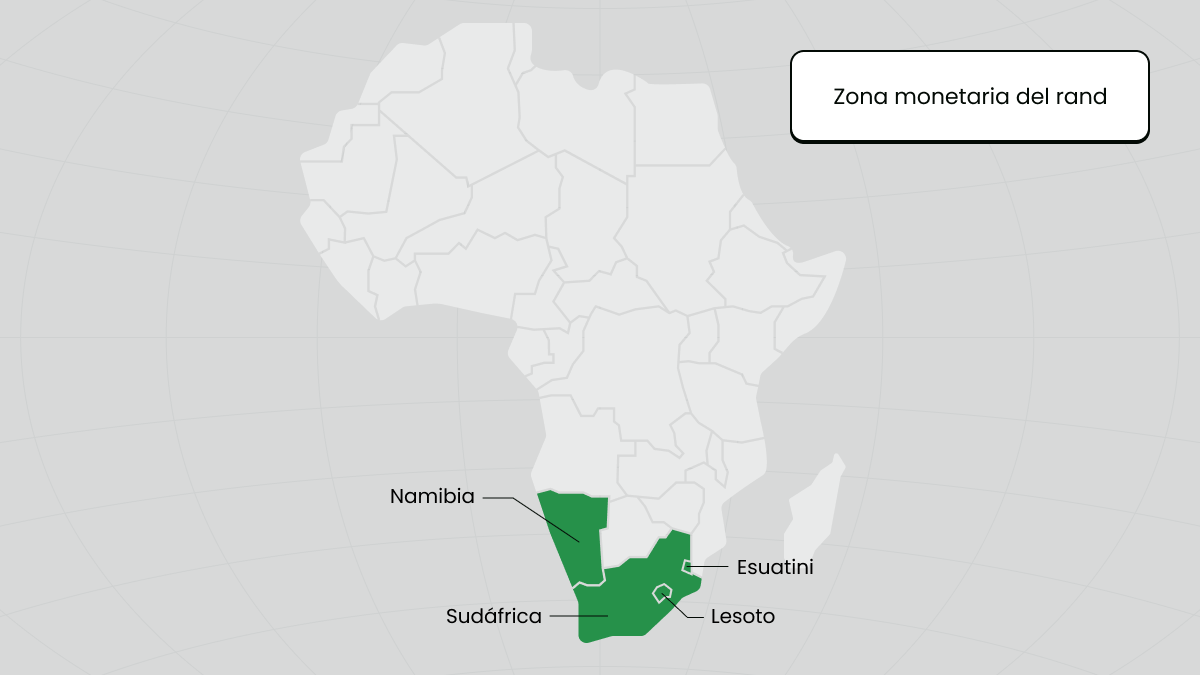
Namibia, Lesotho y Eswatini vinculan sus monedas (el dólar namibio, el loti lesotho y el lilangeni suazi, respectivamente) a la par del rand. Este acuerdo simplifica las transacciones, aumenta la fluidez de los cambios de moneda y estabiliza las economías al reducir los riesgos asociados a las fluctuaciones de las tasas de cambio entre estos países. El CMA promueve la estabilidad económica y refuerza las relaciones financieras entre Sudáfrica y sus países vecinos.
Las fluctuaciones del rand
El rand sudafricano ha experimentado una gran volatilidad y fluctuaciones en su valor a lo largo de las décadas, influido por factores internos y por las condiciones económicas internacionales. En un inicio, tras su introducción en 1961, el rand se comerciaba bastante más que el dólar estadounidense, pero esto cambió a medida que el país se enfrentaba a diversos retos económicos y políticos.
El valor del rand empezó a erosionarse en la década de 1980 debido a la creciente presión internacional contra el régimen del apartheid, las altas tasas de inflación y la incertidumbre política dentro del país. Este declive se acentuó de forma notable después de que el gobierno declarara una moratoria en el pago de la deuda en 1985, lo que provocó una rápida depreciación de la moneda. La era posterior al apartheid trajo consigo una estabilidad inicial, pero el rand sufrió otro duro golpe durante las crisis financieras mundiales y otros descalabros económicos locales. En diciembre de 2001 alcanzó su nivel histórico más bajo, al cotizar a más de 13 rands por dólar estadounidense.
En los últimos años, el rand ha seguido viéndose afectado por la situación económica mundial, los precios de los commodities y los cambios en el panorama político sudafricano. Los traders y analistas siguen de cerca sus fortunas fluctuantes, ya que no solo reflejan la situación económica de Sudáfrica, sino también el entorno general de los mercados emergentes.
¿Por qué la moneda sudafricana se llama ZAR?
La abreviatura 'ZAR' del rand sudafricano procede de la palabra neerlandesa 'Zuid-Afrikaanse Rand'. 'Zuid-Afrikaanse' se traduce como 'sudafricano' en neerlandés, lo que refleja la influencia histórica de la lengua neerlandesa en la región debido al asentamiento y la colonización de los holandeses en el siglo XVII. El término 'rand' procede de Witwatersrand, la cordillera sobre la que se construyó Johannesburgo y donde se descubrieron importantes yacimientos de oro, lo que dio lugar a la fiebre del oro en la zona. Esta característica geológica dio nombre a la moneda y subrayó la importancia económica de la minería del oro para el desarrollo económico de Sudáfrica.
El código ISO 'ZAR' se utiliza en los mercados financieros y en el mundo del trading de divisas para representar el rand sudafricano, distinguiéndolo de otras monedas que utilizan el signo 'R', como el real brasileño.
¿Cuánto vale un rand frente a un dólar?
La tasa de cambio actual entre el rand sudafricano (ZAR) y el dólar estadounidense (USD) es una cifra dinámica sujeta a fluctuaciones influenciadas por las condiciones económicas mundiales y factores locales dentro de Sudáfrica. Según los últimos datos disponibles, la tasa de cambio es de alrededor de 1 USD por 19 ZAR. Esta cotización representa el precio medio de mercado, una referencia estándar para los informes financieros, y representa un equilibrio entre los precios de compra (bid) y de venta (ask) en los mercados de divisas.

Factores que afectan la tasa de cambio:
- Decisiones sobre las tasas de interés de la Fed (Reserva Federal de Estados Unidos) y el SARB: Las decisiones sobre las tasas de interés tanto de la Fed como del SARB son cruciales. Unas tasas de interés más altas fijadas por el SARB pueden atraer capital extranjero, lo que se traduce en un rand más fuerte a medida que los inversores buscan mejores rendimientos. Por el contrario, unas tasas más bajas suelen tener el efecto contrario, haciendo que el ZAR resulte menos atractivo para los inversores extranjeros. Del mismo modo, las decisiones de la Reserva Federal sobre las tasas de interés pueden repercutir de forma indirecta en el ZAR al influir en los flujos financieros mundiales y en la confianza de los inversores.
- Estabilidad política: Los acontecimientos políticos y los cambios de política pueden provocar importantes fluctuaciones de la tasa de cambio, ya que afectan la confianza de los inversores y los pronósticos económicos.
- Precios de los commodities: Sudáfrica es un importante exportador de commodities como el oro, los diamantes y el platino. Cuando los precios de estos commodities se elevan en los mercados mundiales, el ZAR suele fortalecerse debido al aumento de los ingresos procedentes de las exportaciones. Por el contrario, una caída de estos precios puede debilitar el rand.
Preguntas frecuentes
¿Por qué la moneda sudafricana se llama ZAR?
El rand sudafricano se abrevia como ZAR, que significa 'Zuid-Afrikaanse Rand'. Esta abreviatura procede de la palabra neerlandesa para Sudáfrica ('Zuid-Afrika') combinada con la palabra para la moneda ('rand'), lo que refleja la historia del país y sus lenguas oficiales, que incluyen el afrikaans derivado del neerlandés. Este código se utiliza en el análisis y trading financiero para diferenciarla de otras monedas, como el dólar estadounidense. La designación ayuda a agilizar las transacciones en los mercados mundiales de divisas y es reconocida en todo el mundo en contextos empresariales y financieros.
¿Qué caracteriza al rand?
El rand sudafricano es conocido por su volatilidad en los mercados mundiales, influido por factores socioeconómicos internos y por las corrientes financieras internacionales. El valor del rand puede fluctuar de forma significativa debido a cambios en los precios de los commodities, la estabilidad política y los resultados económicos. Esta volatilidad lo convierte en objeto de gran interés y análisis en los círculos financieros y de trading. El rand opera bajo un sistema de tasa de cambio flotante. Su valor puede variar mucho frente a divisas como el USD, lo que lo convierte en un punto de interés para inversores y analistas de los mercados de divisas africanos y mundiales.
¿Qué países vinculan su moneda al rand sudafricano?
Varios países de la región de África Austral vinculan sus monedas al rand sudafricano para estabilizar sus sistemas económicos. Este acuerdo forma parte del Área Monetaria Común (ZMC), que incluye a Lesoto, Namibia y Eswatini (antigua Suazilandia). Al vincular sus monedas al rand, estos países se benefician de un menor riesgo cambiario al comerciar con Sudáfrica, que es la potencia económica de la región. La vinculación de sus monedas favorece el estrechamiento de los lazos económicos y facilita los flujos de inversión y trading dentro de la zona, demostrando el importante papel que desempeña el rand en los mercados financieros africanos.
¿Son lo mismo un rand sudafricano y un Krugerrand?
El rand sudafricano y el krugerrand no son lo mismo. El rand es la moneda oficial de Sudáfrica, utilizada para las transacciones diarias y las mediciones económicas. En cambio, el Krugerrand es una moneda de oro acuñada por primera vez en 1967 para ayudar a comercializar el oro sudafricano. No tiene valor nominal, sino que se opera en función del precio actual del oro en el mercado, y suele ser utilizada por inversores y coleccionistas. Aunque ambas están vinculadas a la historia económica sudafricana, sus usos en el sector financiero y el trading son muy diferentes: el Krugerrand sirve, sobre todo, como vehículo de inversión en oro.
En resumen
El rand sudafricano (ZAR) es más que una moneda: refleja la trayectoria histórica, política y económica de la nación. Para los traders de divisas y los inversores, comprender los matices del rand es crucial debido a su volatilidad significativa y a la influencia de los acontecimientos económicos tanto locales como mundiales. La divisa es un barómetro del sentimiento de los inversores en los mercados emergentes y ofrece oportunidades y riesgos únicos. Los traders que comprenden los contextos económicos históricos y actuales que influyen en el rand pueden aprovechar estos conocimientos para aplicar estrategias de trading informadas en el mercado de divisas.
Conclusión
Desde sus orígenes en los ricos yacimientos auríferos de Witwatersrand hasta su papel actual en el entorno del trading mundial, el rand sudafricano tiene una larga historia entrelazada con las fortunas de su nación. A medida que Sudáfrica siga evolucionando en los rubros de la política y la economía, el rand seguirá siendo una divisa clave para quienes se dedican al trading y las finanzas globales. Comprender su pasado y los factores que influyen en su valor actual es esencial para cualquiera que desee participar o invertir en los mercados emergentes.