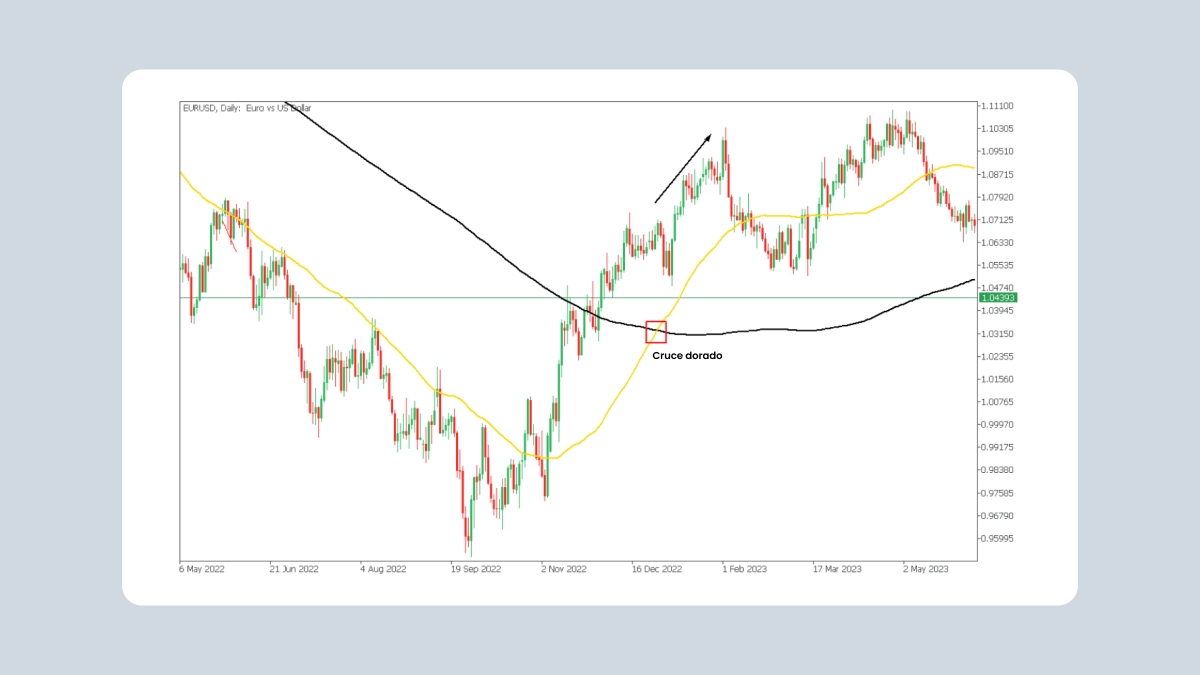
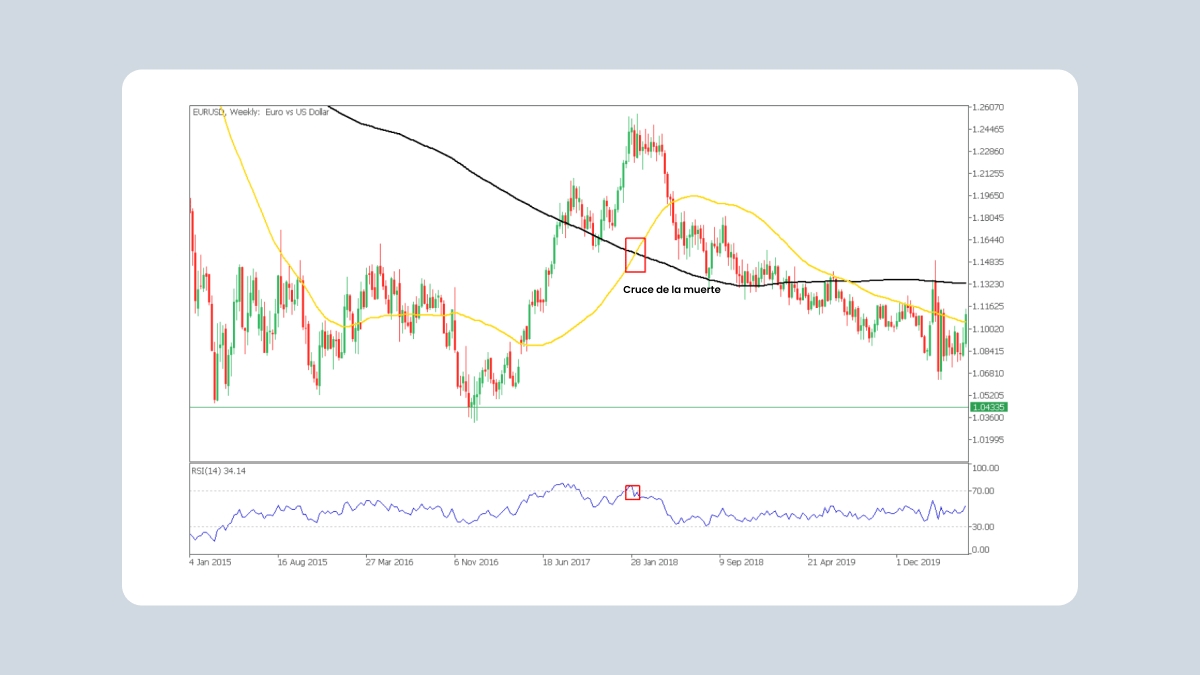
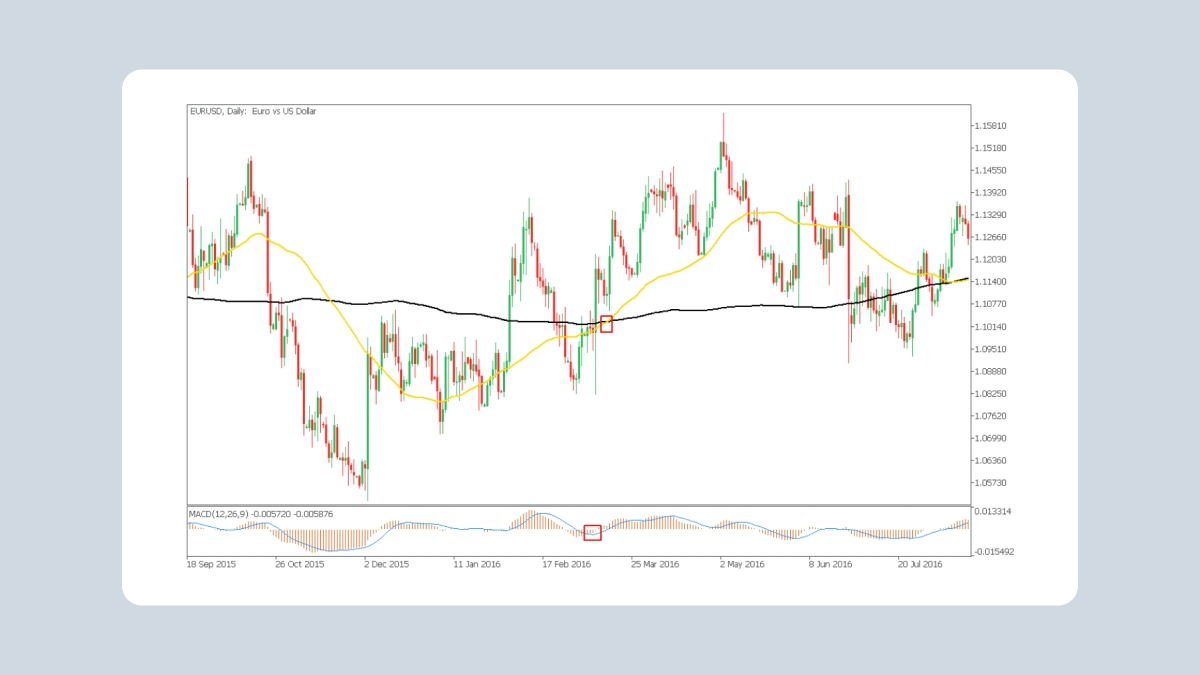
3. Bandas de Bollinger
Las bandas de Bollinger incluyen la volatilidad al envolver los precios dentro de las bandas inferior y superior. Si los precios rompen la banda superior después de un cruce alcista de MA, los traders interpretan esto como un fuerte impulso al alza. Por otro lado, las bandas en contracción junto con una ruptura de la MA indican la posibilidad inminente de un cambio significativo en el precio.
Aplicaciones prácticas
En todas las clases de activos, las medias móviles ofrecen un valor constante.
Estrategia en Forex
Imagina a un trader analizando el par de divisas USDJPY. Una EMA de 20 días junto con una WMA de 50 días muestra que el par tiene una tendencia al alza. Cuando la EMA de 20 días cruza por encima de la WMA de 50 días, junto con el precio que se aferra al límite superior de las envolturas de media móvil, el trader ve una oportunidad de compra óptima.
Mercado de valores
Considera un escenario donde una acción biotecnológica se consolida justo por debajo de su SMA de 200 días. Después de una serie de noticias positivas, el precio rompe drásticamente por encima de la SMA de 200 días en alto volumen, lo que indica un poderoso rally de ruptura. Los traders pueden usar este movimiento para establecer posiciones largas, confiando en que el impulso hará que las acciones suban.
Limitaciones de las medias móviles
A pesar de sus muchas ventajas, las medias móviles tienen limitaciones. Al depender de datos históricos son indicadores rezagados, que a menudo ofrecen señales después de que la tendencia ya ha comenzado.
Además, en los mercados de rango limitado o laterales, las MA pueden generar señales engañosas, con precios que cruzan repetidamente la MA sin establecer una dirección firme.
Para mitigar estos desafíos, los traders pueden extender las temporalidades para reducir el impacto del ruido o combinar medias móviles con otros indicadores, como el análisis de volumen, para pulir los datos del mercado. El análisis fundamental puede complementar aún más las MA, ofreciendo una imagen del mercado más completa.
Resumen
Las medias móviles son los pilares del análisis técnico, ya que ofrecen claridad en mercados complejos y guían a los traders hacia decisiones más informadas. Dominar las aplicaciones matizadas de las MA, ya sea a través de técnicas simples, estrategias avanzadas o combinaciones de indicadores, puede ayudarte a desarrollar una ventaja en el trading.
Al comprender las fortalezas y limitaciones, estarás mejor preparado para aprovechar su máximo potencial, sin importar tu estilo de trading o el mercado que elijas. Usar las medias móviles junto con un análisis sólido y gestión de riesgos te dará la confianza para enfrentar con precisión incluso las condiciones de mercado más difíciles.
.jpg)