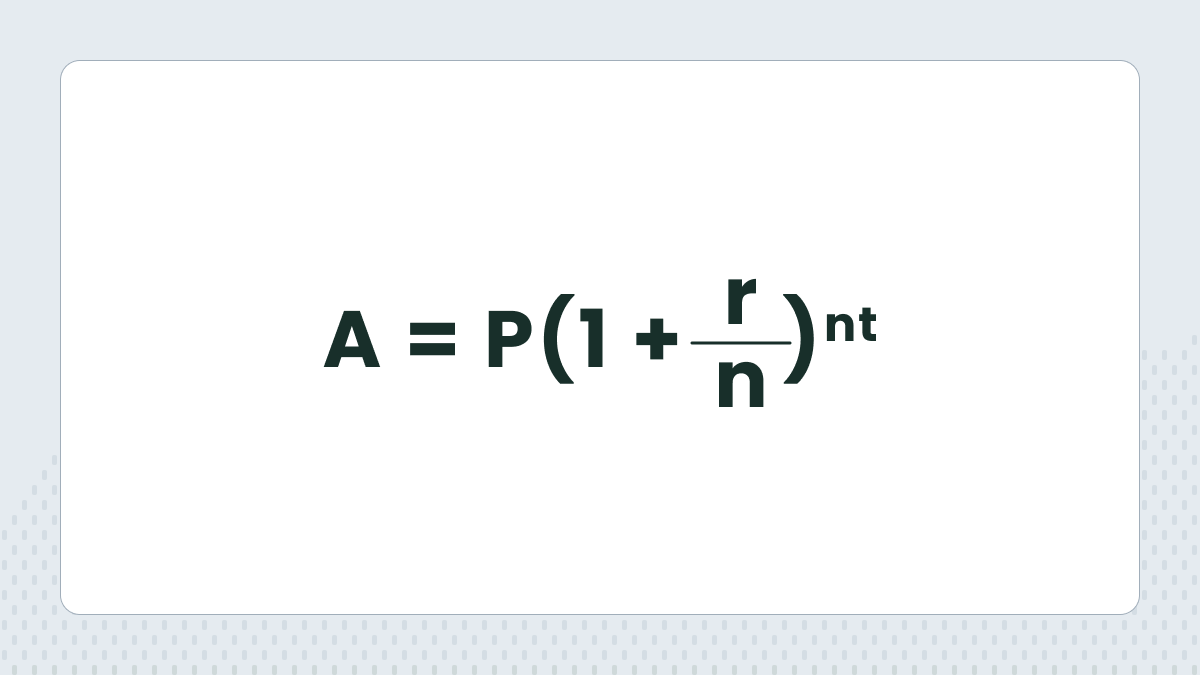Simple or compound interest — what will give you more profit? In this article we explore simple and compound interest, examine their pros and cons, and highlight the key differences between them. You will learn how they are calculated, the advantages they offer, and when it’s most appropriate to use each type.
Types of interest
What is interest? It’s the money you pay or earn by borrowing or investing, calculated as a percentage of the borrowed or saved amount. There are several types of interest, each serving different purposes and suiting different financial situations. Understanding their specific uses helps people make better financial decisions.
Interest can be fixed or variable, amortized, nominal, effective, precomputed, or discount, but the most common types are simple and compound interest rates.
Definition of simple interest
What is simple interest?
Simple interest is added only to the principal — the original amount of money borrowed or invested. Simple interest does not include any interest that has been added over time. In terms of calculation, it is the most straightforward and uncomplicated type of interest.
Formula for simple interest and explanation of variables (P, r, t)
To calculate a simple interest, use this formula: A=P(1+rt).
Let’s break down the variables.
P — the principal: the original amount of money you deposit or borrow.
r — the interest rate: the percentage charged or earned per year (expressed as a decimal number, e.g. 7% would be written as 0.07).
t — the time in years, over which the interest is added.
A — the total sum.
Example of simple interest calculation
If you deposit $1000 at a 5% interest rate, in three years you will have $1150. Let’s replace the variables with the numbers:
P — 1000;
r — 0.05;
t — 3.
If we use the formula, the total sum (A) is 1150, because 1000(1+(0.05×3))=1150.
Pros and cons of simple interest

Consider the benefits and drawbacks of each type of interest before making a decision.
On the one hand, simple interest has certain perks:
it’s straightforward and easy to calculate;
the payments are predictable as the interest stays the same over time;
you pay less if it is a short-term loan.
On the other, it also has some disadvantages:
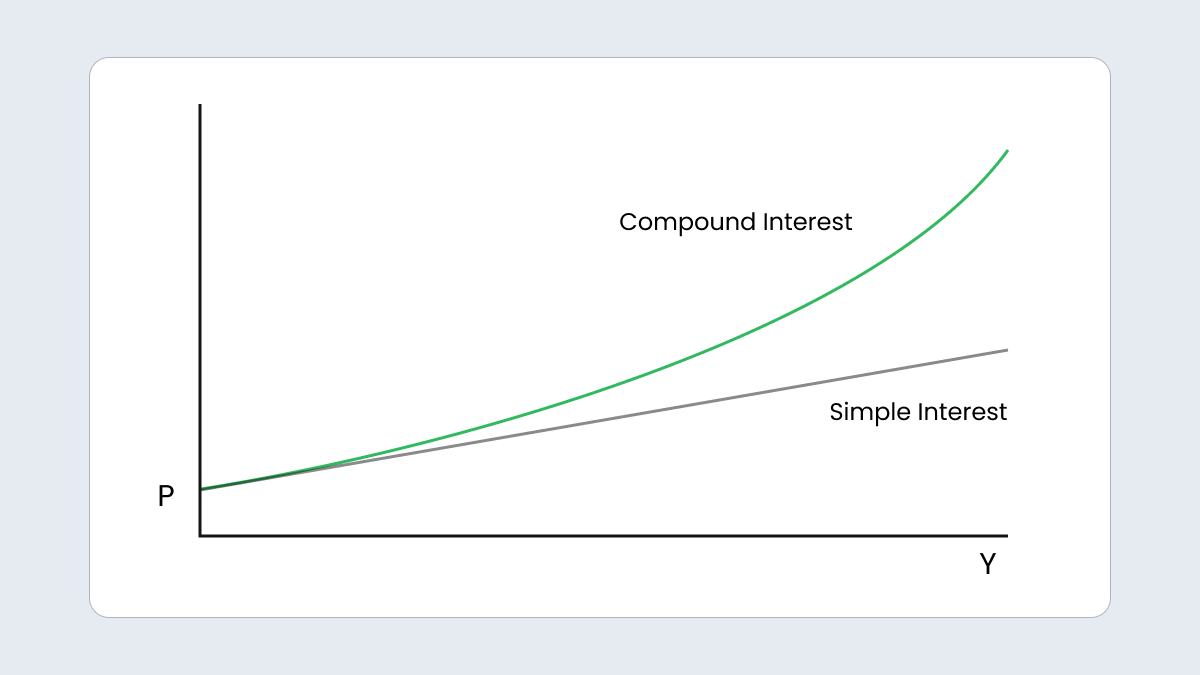
it is less profitable in case of a long-term investment;
the accumulated interest of the investment can’t bring you profit, because you can’t reinvest it.
Looking for new ways to grow your wealth? Open a demo account at FBS!